|
TOPICS
Accent and Accent-Marking in Ancient Greek
Contonation and Mora
The Last 3 Syllables and the Accents
•acute
•circumflex
•grave
•ultima
•penult
•antepenult
•more examples
Proclitics
Enclitics
Multiple Clitics
Traditional Terminology
Persistent Accentuation
• a- and o-declension
• consonant declension
Recessive Accentuation
|
Persistent Accentuation (4 of 7): examples for a-declension |
Previous | Next |
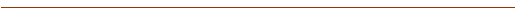 |
| γνώμη |
acute on P in nom. sing. (“main form”) |
| γνώμης |
acute persists on P |
| γνώμῃ |
acute persists on P |
| γνώμην |
acute persists on P |
| γνώμη |
acute persists on P |
| γνῶμαι |
accent persists on P, but circumflex because of short U (final αι counts as short) – rule 2 |
| γνωμῶν |
circumflex on U of genitive plural of all a-declension nouns – rule 3 |
| γνώμαις |
acute persists on P (αι with ς following is not final, so counts as long) |
| γνώμᾱς |
acute persists on P |
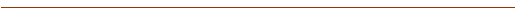
Feminine forms from the adjective ἄξιος, ἀξίᾱ, ἄξιον
| ἀξίᾱ |
acute moves to P from A because of long U (“main form” nom. sing. masc. has acute on A with short U) |
| ἀξίᾱς |
acute moves to P from A because of long U |
| ἀξίᾳ |
acute moves to P from A because of long U |
| ἀξίᾱν |
acute moves to P from A because of long U |
| ἀξίᾱ |
acute moves to P from A because of long U |
| ἄξιαι |
acute persists on A (final αι counts as short) |
| ἀξίων |
acute moves to P from A because of long U |
| ἀξίαις |
acute moves to P from A because of long U (αι with ς following is not final, so counts as long) |
| ἀξίᾱς |
acute moves to P from A because of long U |
| |
NOTE: if this were the noun ἀξίᾱ, ἀξίᾱς, then the genitive plural would be accented ἀξιῶν by rule 3. |
|
 Accentuation Tutorial
Accentuation Tutorial
